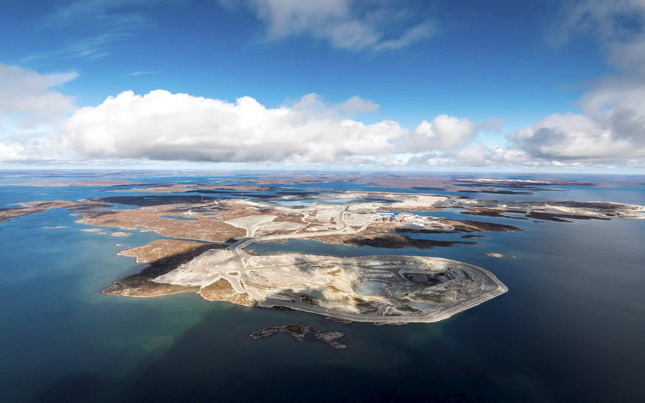
Namibia is one of Africa’s top five diamond exporters, right behind Angola, Botswana, and South Africa. In 2022, the country exported more than $940 million worth of diamonds.
The world’s demand for natural diamonds has bounced back from a slump during the COVID-19 pandemic, with Namibia’s largest marine dining company, Debmarine, reporting a sales increase of 83% in 2022 from the previous year.
Still, Debmarine CEO Willy Mertens is worried about competition from synthetic diamonds, sector of the business that could cost many Namibians their jobs.
Though trained jewelers can tell the difference between lab-grown and natural diamonds, there’s nothing obvious to distinguish lab-grown diamonds from natural ones.
The Modern Mining publication recently said that in 2022, lab-grown diamond jewelry surpassed 10% of the market of global jewelry sales for the first time. The publication said artificial diamond sales are forecast to continue growing at an annual double-digit percentage rate in coming years.
Namibia, where workers extracted 2.1 million carats in diamonds in 2022, is embarking on a campaign to tout natural diamonds as environmentally sound and holding greater value for the money.
“We’ve seen in the past couple of years that lab-grown diamonds, or synthetics as you call them, have sort of infiltrated the natural diamond market,” said Mertens. ” … people were first marketing them as real diamonds and we’ve done a lot of work around trying to differentiate them.”
One of the challenges of marketing Namibian natural diamonds is the environmental impact that diamonds have on the landscape.
Mertens said Debmarine invests a significant amount of its profits into environmental rehabilitation and restoration of landscapes and the seabed damaged by mining.
“The restoration of the seabed actually happens naturally as the waves move,” Mertens said. “So what we are doing is that we are monitoring that, and what we do is we mine out a specific area and we leave an area next to it vacant, and over time we monitor how the area where we have recovered diamonds looks like compared to the one that was not touched and we’ve seen that it takes about three to 10 years maximum for that to completely restore. By completely restoring, mean about 70% of the organisms have returned to that place. On the land, it is sand that we are moving and what we do now is that we are using that same sand to keep the sea walls in tact.”
Mertens recently paid a courtesy call on Namibian President Nangolo Mbumba, to introduce the De Beers global ambassador for natural diamonds, Hollywood actor Lupita Nyong’o, and talk to the president about challenges facing Namibia’s diamond industry.
De Beers Natural Diamonds Global Ambassador Lupita Nyong’o, left, Namibia President Nangolo Mbumba, center, and Debmarine CEO Willy Mertens in Windhoek, Namibia, July 19, 2024. (Vitalio Angula/VOA)
De Beers Natural Diamonds Global Ambassador Lupita Nyong’o, left, Namibia President Nangolo Mbumba, center, and Debmarine CEO Willy Mertens in Windhoek, Namibia, July 19, 2024. (Vitalio Angula/VOA)
President Mbumba lamented a proposal for the Kimberley process — the process meant to screen out so-called “conflict diamonds” from entering the international market — to begin certifying all diamonds in Antwerp, Belgium.
The Group of Seven largest economies said that is an effort to prevent Russian diamonds from being sold abroad.
Mbumba said the measure would hurt African diamond producers.
“Recently, the decision was made by the G7 countries to route all rough and polished diamonds destined for G7 countries via Belgium,” said Mbumba. “This decision poses a serious risk and threat to our economies, especially the economies of Angola, Botswana and Namibia by increasing the cost as well as curtailing freedom of trade for our countries’ products.”
Namibia’s president said he and his counterparts from Angola and Botswana have written a letter to the G7 to ask them to halt their plans.
Source: voanews