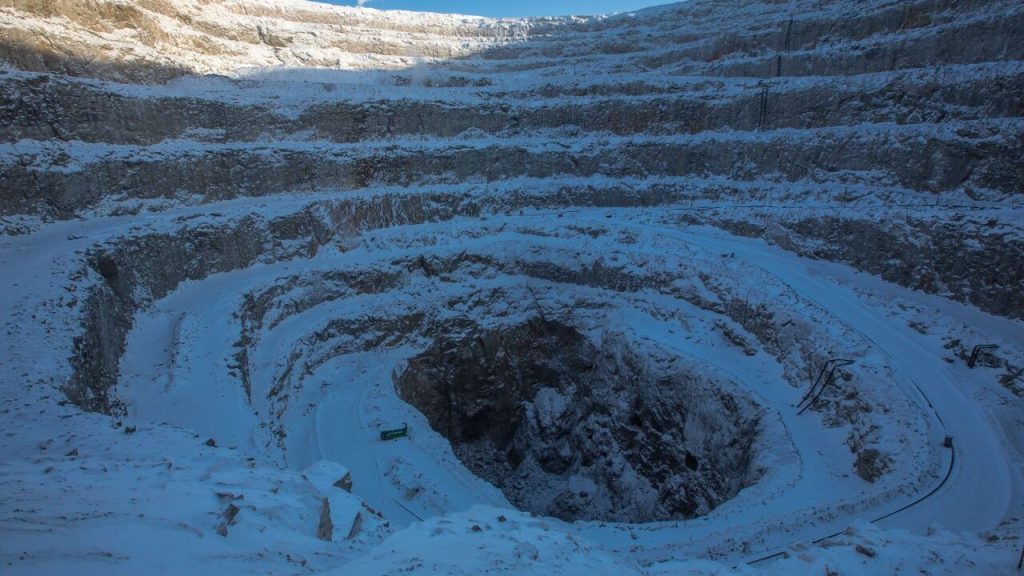
Rio Tinto’s diamond production fell in 2023 following the closure of portions of its Diavik mine in Canada earlier in the year.
Total production dropped 28% to 3.3 million carats for the full year, the company said Tuesday. Rio Tinto completed mining at Diavik’s A418 underground area and at its A21 open-pit kimberlite pipes, it explained. Improvements in the volume of ore produced at the A154N underground partially offset the loss in output from those portions.
In the fourth quarter, output slipped 50% year on year to 659,000 carats, and was down 13% from the previous quarter.
Diavik is Rio Tinto’s sole diamond mine following the closure of Australia’s Argyle deposit in November 2020. The miner’s share of Diavik increased from 60% to 100% in November 2021, when it assumed control of the asset following the inability of its joint-venture partner, Dominion Diamond Mines, to pay its share of upkeep. In November, Rio Tinto also sold its 75% share of the Fort à la Corne diamond exploration project in Saskatchewan to joint-venture partner Star Diamond Corporation, in an effort to focus on metals and minerals.
Rio Tinto will spend $40 million to move into underground mining at the A21 portion of Diavik, which it believes could add more than 2 million carats of rough production, it reported in February 2023. That expansion is due to keep the mine in operation until the first quarter of 2026.
Meanwhile, the company did not provide rough-production guidance for 2024.
Source: Diamonds.net