
The Fancy Colour Diamond Index for the third quarter of 2017 indicates a slight rise overall of 0.2 percent over Q2 2017, for yellow, pink and blue fancy colour diamonds in all sizes and saturations.
Moreover, the index shows that in Q3 prices of fancy blue and pink colour diamonds appreciated 0.4 percent and 0.3 percent respectively. Similar to Q1 2017 trends, the strongest performing price categories during Q3 2017 were fancy intense and fancy vivid blue diamonds across all carat sizes.
In Q3 2017, fancy yellow diamond prices declined by 0.1 percent, the lowest price decrease for the category since Q3 2016. There was price stability across most other fancy colour diamond categories, continuing the trend in fancy colour diamond pricing patterns during 2016 and early 2017.
On a year-on-year basis, when compared to Q3 2016, the Fancy Colour Diamond Index is slightly down by 0.2 percent, with fancy blues up 4.7 percent and fancy yellows and fancy pinks down 2.5 percent and 0.6 percent, respectively. Compared to the same period in 2015, the Fancy Colour Diamond Index is up 0.7 percent with fancy blues and fancy pinks up 8.1 percent and 1.2 percent respectively, and fancy yellows down 4.1 percent.
The Fancy Colour Diamond Index is published by the non-profit Fancy Colour Research Foundation (FCRF), and tracks pricing data for yellow, pink and blue fancy colour diamonds in three key global trading centers – Hong Kong, New York and Tel Aviv.
FCRF Advisory Board Chairman Eden Rachminov said: “As far as supply is concerned, 2017 and the year before were record low years for blue fancy colour diamond production from mines. The majority of the blues that are coming into the market are pre-owned stones. Manufacturers have seen a significant drop in availability across all sizes and qualities, and consequently prices have continued to increase. Going forward, the market will have to adjust to a lower “new normal” supply level for blue fancy colour and pinks in the high saturations levels.”
Source: idexonline
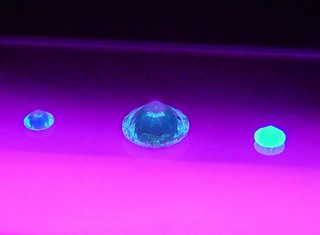
There is common misconception that a diamond exhibiting fluorescence under ultra violet light has some kind of colour defect or transparency issue.
This NOT true at all. The naturally occurring fluorescence phenomenon is a unique completely hidden feature, which is present to some level in approximately 30% of all diamonds.
The effect is seen in Diamonds which have Carbon bonds which include boron.
Boron causes the diamond to glow when held under a powerful ultra violet light also known as blacklight.
The amount of boron in the Carbon bond making up the diamond will determine the level of fluorescence. Fluorescence is rated by the Laboratory as Very Strong, Strong, Medium, Faint, None. This relates to the strength of the fluorescent glow under ultra violet light.
Laboratories use fluorescence as a means of identifying the diamond along with many other characteristics found in natural diamonds.
May Jewellers and consumers have been led to believe that fluorescence in diamonds will negatively affect the colour or transparency.
Again this is NOT true. Fluorescence has a tendency to make the middle to lower colour diamonds in the colour chart look whiter than the same colour would with no fluorescence. More obvious when viewing the diamond from the table view or top.
Therefore fluorescence has very little, to no negative effect on the diamonds colour or transparency. Diamonds are more likely affected by heavy graining or microscopic clouds.
This is good for the buyer as misinformation has caused consumers to be wary of a UV responsive or fluorescence diamond. This has caused diamond dealers and jewellers to discount these diamonds based on the level of fluorescence in the diamond the same colour and clarity.
Conclusion: save some money and take advantage of the lack of knowledge in the market.
Sarine Technologies the world leader in diamond measuring and assessing is expanding its diamond report. It will include the 4C’s quality grades including the diamond’s cut, color, clarity and carat weight. This will be done using its own automated grading tools.
To get these grades for the diamonds Sarine is using its Clarity and Colour machines unveiled last year.. The two machines can automatically measure a diamond’s clarity and color, a skill usually performed by trained gemologists in laboratories like the GIA, HRD, DCLA and others.
Sarine claims it can deliver quality diamond grading with less subjectivity and fewer human errors, adding that the move would raise confidence.
Sarine is collaborating with Swiss gemological lab GGTL Laboratories on the technology.



