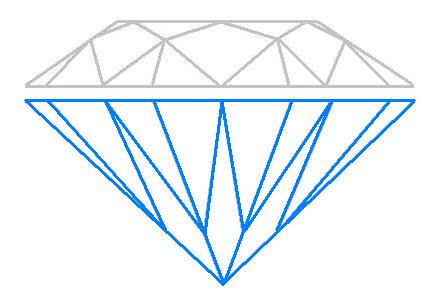
Pavilion Depth Percentage
The pavilion depth percentage is a crucial measurement in understanding how well a diamond performs in terms[…]
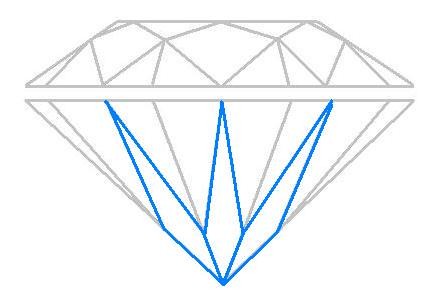
Pavilion Main Facets
The pavilion main facets are a crucial component of a diamond’s pavilion, contributing significantly to its overall[…]

Pavilion Angle
The pavilion angle is a key proportion in diamond cutting, referring to the angle between the girdle[…]
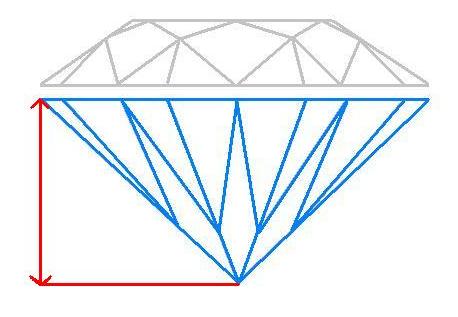
Pavilion Depth
The pavilion depth refers to the vertical distance from the girdle (the widest part of the diamond)[…]
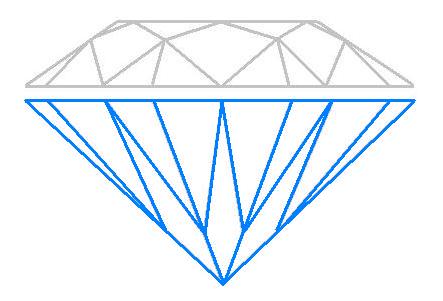
Pavilion
The pavilion is the lower portion of a diamond, extending from the girdle (the widest part) of[…]

Old Mine Cut
The Old Mine Cut is a historical diamond cut, first popularized in the 18th and 19th centuries.

Octahedron
An octahedron is one of the most sought-after crystal shapes for rough diamonds, featuring eight triangular faces[…]



