Flash Effect in Fracture-Filled Diamonds: What It Is and How It Affects Sparkle
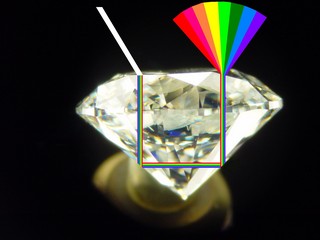
The flash effect in a fracture-filled diamond refers to the dispersion of light and the sparkle that occurs as the diamond is moved or rotated, much like in any other diamond. However, in fracture-filled diamonds, the flash effect can be influenced by the quality and extent of the fracture filling, as well as how the filling interacts with light within the diamond.
What Are Fracture-Filled Diamonds?
Fracture-filled diamonds are diamonds that have invisible fractures or cracks that have been filled with a substance, typically glass or a resin, to improve the diamond’s appearance. The filling material helps to mask the appearance of these inclusions, making the diamond look cleaner and less affected by visible cracks or fractures.
However, while this treatment can improve clarity and overall appearance, it can have implications for the diamond’s optical properties, including its flash effect.
How the Flash Effect Works in Fracture-Filled Diamonds
Light Reflection and Dispersion:
The flash effect in a diamond occurs when light enters the stone and reflects off the facets, creating flashes of sparkle. In fracture-filled diamonds, the filling material in the cracks can interact with the light and change the way it reflects and refracts within the diamond.
Impact of Filling Material:
Glass or resin fillings typically have a different refractive index than the surrounding diamond. This means that the refraction and dispersion of light may not be as perfect as in a natural, untreated diamond, potentially affecting the flash effect.
The filling material may cause light to scatter or reflect in ways that slightly diminish the brilliance or fire of the diamond, reducing the intensity of the flash effect.
Filling Quality:
If the fracture filling is of poor quality or is visible under magnification, it may detract from the diamond’s overall appearance, including the flash effect.
High-quality fracture fillings that are carefully done may have less of an impact on the flash effect, but there could still be minor differences in how light behaves within the diamond.
How the Flash Effect Can Be Affected in Fracture-Filled Diamonds
Less Brilliance and Fire:
Due to the difference in the refractive index between the diamond and the filling material, the flash effect in a fracture-filled diamond might be duller compared to an untreated diamond. This can lead to reduced brilliance and fire, making the diamond less vibrant under direct light.
Appearance of the Flash:
The flashes of light may not appear as crisp or vivid because of the altered light paths caused by the filling material in the cracks. In some cases, the fractures can also distort the light, affecting the overall sparkle of the diamond.
Potential Visual Distractions:
In some fracture-filled diamonds, if the filling material is not completely smooth or if it has impurities, it could affect the clarity and lead to visible inclusions or dark spots that might distract from the overall flash effect.
How to Maximize Flash Effect in Fracture-Filled Diamonds
Choose High-Quality Fracture Fillings:
Make sure that the fracture filling has been performed to a high standard and does not detract from the diamond’s optical properties. High-quality fillings will have less of an impact on the flash effect.
Inspect the Diamond Under Different Lighting:
Since the flash effect is more pronounced under bright, direct light, examine the diamond in different lighting conditions to evaluate its sparkle and fire. This will help determine whether the fracture filling is significantly affecting the diamond’s performance.
Consider the Cut:
A well-cut fracture-filled diamond will still produce more sparkle and flash effect compared to a poorly cut one. Pay attention to the cut quality to ensure that the diamond maximizes its brilliance despite the fracture filling.