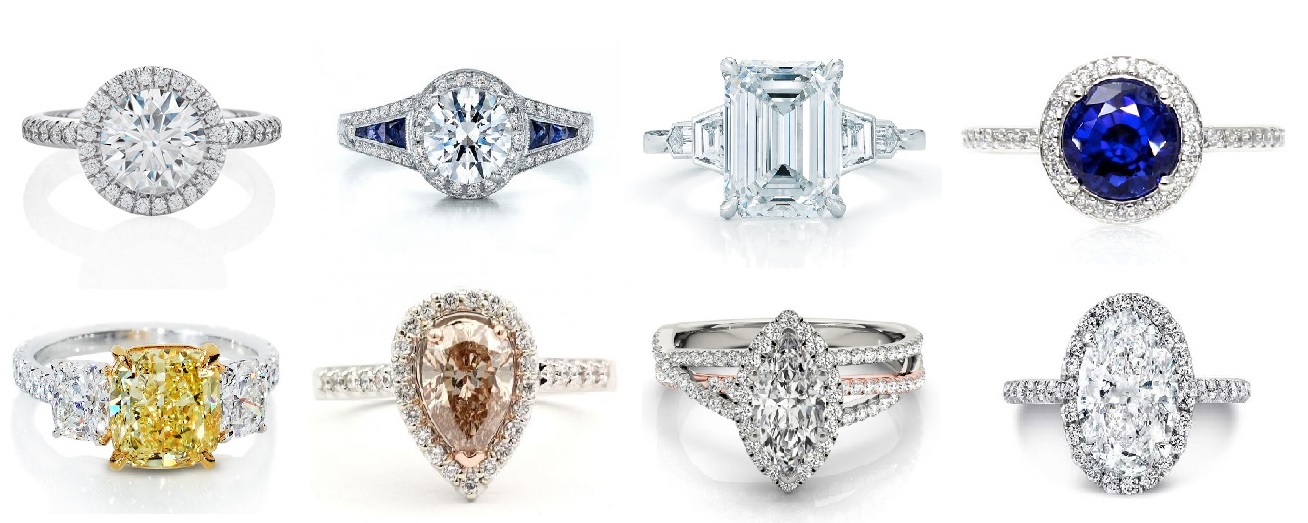
In the context of diamonds, shape refers to the basic outline or form of a polished diamond, which is distinct from its cut (which pertains to the diamond’s facets, proportions, and overall craftsmanship). The shape is the fundamental, overall geometry of the diamond, determining its appearance and how it interacts with light. The shape of a diamond is typically selected based on personal preference, aesthetic taste, and desired brilliance, as different shapes have different effects on the way a diamond reflects light and sparkles.
Types of Diamond Shapes
There are several common diamond shapes, each with unique characteristics, and they vary in terms of their appearance, the way they reflect light, and their overall style. Below are some of the most popular diamond shapes:
Round:
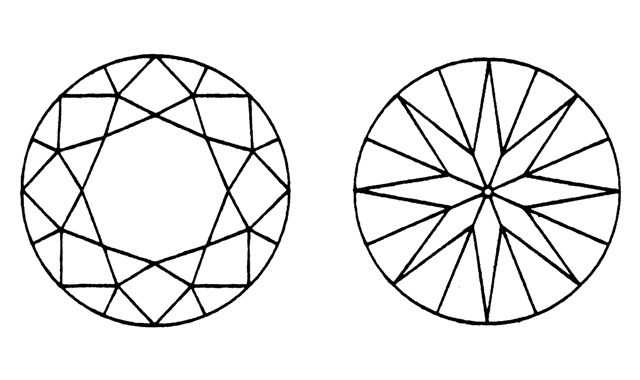
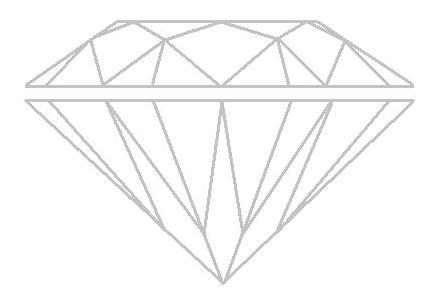
The round shape is the most popular and traditional diamond shape, known for its exceptional brilliance and sparkle. It has a circular outline and is cut with 57 or 58 facets, including the table, crown, pavilion, and girdle. This shape maximises light reflection, making it the most sought-after shape for engagement rings and other jewellery.
The round shape is also known as the round brilliant cut, which is designed to achieve the highest level of brilliance and scintillation, making it the benchmark for diamond cutting.
Princess:
The princess shape is a square or rectangular diamond with pointed corners. It is the second most popular diamond shape after the round shape and is prized for its sharp, modern appearance. Princess cut diamonds have a brilliant faceting style, offering excellent sparkle. This shape is often selected for engagement rings and other jewellery due to its versatile and elegant appearance.
This shape is known for its clean lines, and it’s often favoured by those who want the brilliance of a round diamond but prefer a more angular look.
Emerald:
The emerald shape is a rectangular diamond with cut corners and a step-cut faceting style. Unlike the brilliant cuts, emerald cut diamonds are more about clarity and the stone’s internal characteristics, showcasing the diamond’s clarity through large, open facets.
The emerald shape is known for its elegance, producing a sleek and sophisticated look. It is particularly suited for those who appreciate a vintage style or want a more subtle, understated sparkle compared to the brilliance of other cuts.
Cushion:
The cushion shape is a square or rectangular diamond with rounded corners, giving it a pillow-like appearance. This shape combines features of both the round brilliant and emerald cut, offering a balance of brilliance and clarity.
The cushion shape has a romantic, vintage appeal and is known for its soft, gentle curves. This shape has become increasingly popular in recent years, especially in antique-style jewellery.
Oval:
The oval shape is an elongated round diamond, offering the same brilliance as a round diamond but with an elongated, oval outline. This shape creates the illusion of a larger stone due to its elongated shape and is often chosen for its ability to make fingers appear more slender.
Oval diamonds are known for their classic elegance and sparkling appearance. The elongated form gives a sense of modernity, and it works well in many jewellery settings, particularly for engagement rings.
Marquise:
The marquise shape is a football-like or boat-shaped diamond, with pointed ends and a long, elongated outline. This shape is known for creating the illusion of length and size, making it appear larger than other shapes of the same carat weight.
Marquise diamonds are ideal for creating a bold, dramatic look and are often used in statement pieces or vintage-inspired designs.
Pear:
The pear shape is a combination of round and marquise cuts, with one pointed end and one rounded end, resembling a teardrop. This shape has a soft, elegant look and is often seen in pendants, earrings, and engagement rings.
The pear shape is known for its flattering effect on the hand or neck, as its elongated shape can make the fingers or neckline appear more slender. It also offers a unique balance of brilliance and elegance.
Asscher:
The asscher shape is a square version of the emerald cut, with cut corners and a distinctive step-cut faceting. This shape has a vintage appeal, often associated with the early 20th century and the art deco period.
The asscher shape is known for its regal, sophisticated look and clarity, emphasising the diamond’s natural beauty and internal characteristics. It’s a great choice for those who enjoy vintage or retro styles.
Radiant:
The radiant shape is a square or rectangular diamond with cut corners, combining the brilliance of a round cut with the elegance of an emerald cut. The facets of a radiant diamond are typically more brilliant, giving the stone a striking sparkle while retaining its structured outline.
Radiant diamonds are popular for their modern appeal and versatility, working well in many types of jewellery, from engagement rings to statement necklaces.
Heart:
The heart shape is a romantic, symbolic diamond shape, resembling a heart. It’s a modified brilliant cut, and it’s often selected for engagement rings and valentine’s jewellery due to its emotional significance.
Heart-shaped diamonds combine both brilliance and emotional appeal, and they are often used in pendants, rings, and earrings for special occasions.
Factors Influencing Diamond Shape Selection
When choosing a diamond shape, several factors should be considered:
Personal Taste: The aesthetic preference of the buyer plays a crucial role in selecting the shape. Some may prefer the classic brilliance of the round shape, while others may gravitate towards the elegance of the emerald or the romance of the heart.
Brilliance: Different shapes have varying levels of brilliance. Round diamonds generally offer the highest level of brilliance, while step-cut diamonds (like emerald and asscher) may offer less sparkle but more emphasis on clarity.
Finger Shape and Size: Some diamond shapes, like the oval and marquise, can make fingers appear longer and slender, while other shapes, like cushion or round, may have a more balanced look.
Diamond Setting: The shape of the diamond affects the type of setting it can be used with. Round diamonds fit most settings, but fancy-shaped diamonds, like pear or heart, may require more custom settings to highlight their unique outlines.
Size Appearance: Some diamond shapes, like marquise and pear, can create the illusion of a larger diamond, which may be preferred for those looking for a bigger appearance without increasing carat weight.
The shape of a diamond is a fundamental factor in its overall appearance and appeal. Each shape offers its own unique style, brilliance, and aesthetic qualities, allowing buyers to select the diamond that best reflects their personal tastes, lifestyle, and the intended jewellery setting. Whether opting for the timeless round or the elegant emerald, each shape offers something special, making it an essential element in choosing the perfect diamond.