Eye-Clean Diamond: Understanding Clarity
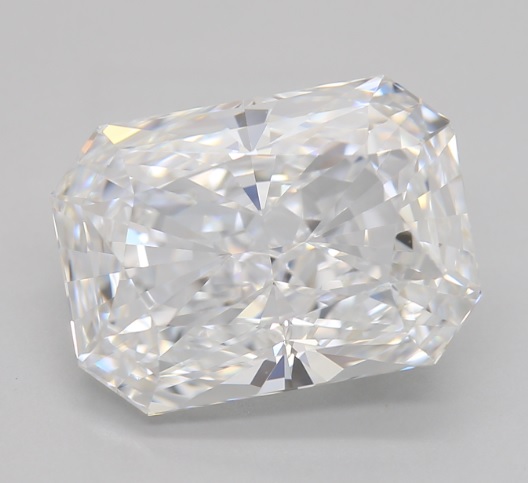
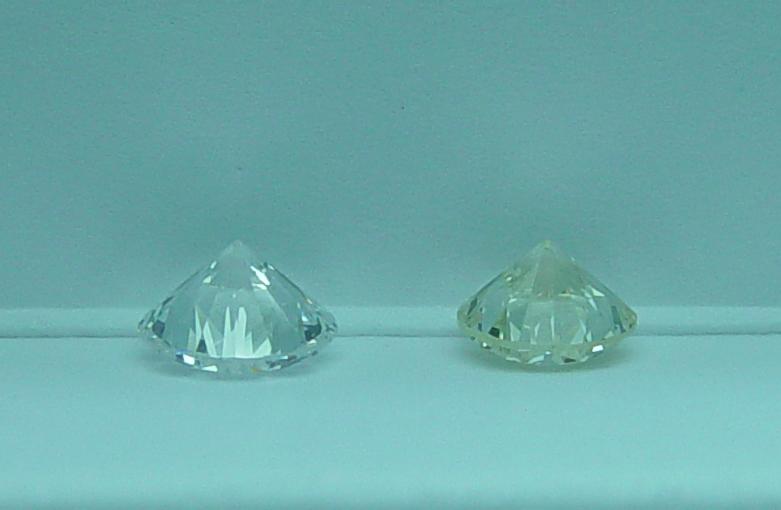
An eye-clean diamond refers to a diamond that has no visible inclusions or blemishes when viewed with the naked eye from a standard viewing distance (about 15–30 cm). This term is important in diamond clarity grading, as it helps buyers choose diamonds that appear flawless without the high cost of an internally flawless (IF) or very high-clarity grade stone.
Key Factors in Eye-Clean Diamonds
Diamond Clarity Grades & Eye-Clean Standards
FL (Flawless) & IF (Internally Flawless) – Always eye-clean (no inclusions even under magnification).
VVS1 & VVS2 (Very, Very Slightly Included) – Essentially eye-clean, with inclusions only visible under 10x magnification.
VS1 & VS2 (Very Slightly Included) – Generally eye-clean, with VS2 possibly showing inclusions in larger stones (2.00+ carats).
SI1 (Slightly Included 1) – May be eye-clean, but some stones might have visible inclusions. Careful selection is needed.
SI2 & I1 (Included 1) – Typically not eye-clean; inclusions are often visible without magnification.
I2 & I3 (Heavily Included) – Clearly visible inclusions that affect beauty and durability.
Size & Location of Inclusions
Inclusions near the edges (girdle) are less noticeable than those under the table (center of the diamond).
White or faint inclusions (like feathers or clouds) blend better than dark or black inclusions.
Smaller diamonds (under 1.00 ct) tend to be more eye-clean at lower clarity grades than larger diamonds.
Diamond Cut & Brilliance
Brilliant cuts (Round, Cushion, Princess, Radiant) can mask inclusions due to their sparkle.
Step cuts (Emerald, Asscher) reveal inclusions more easily because of their open faceting style.