Girdle Thickness: Importance in Diamond Cut & Durability
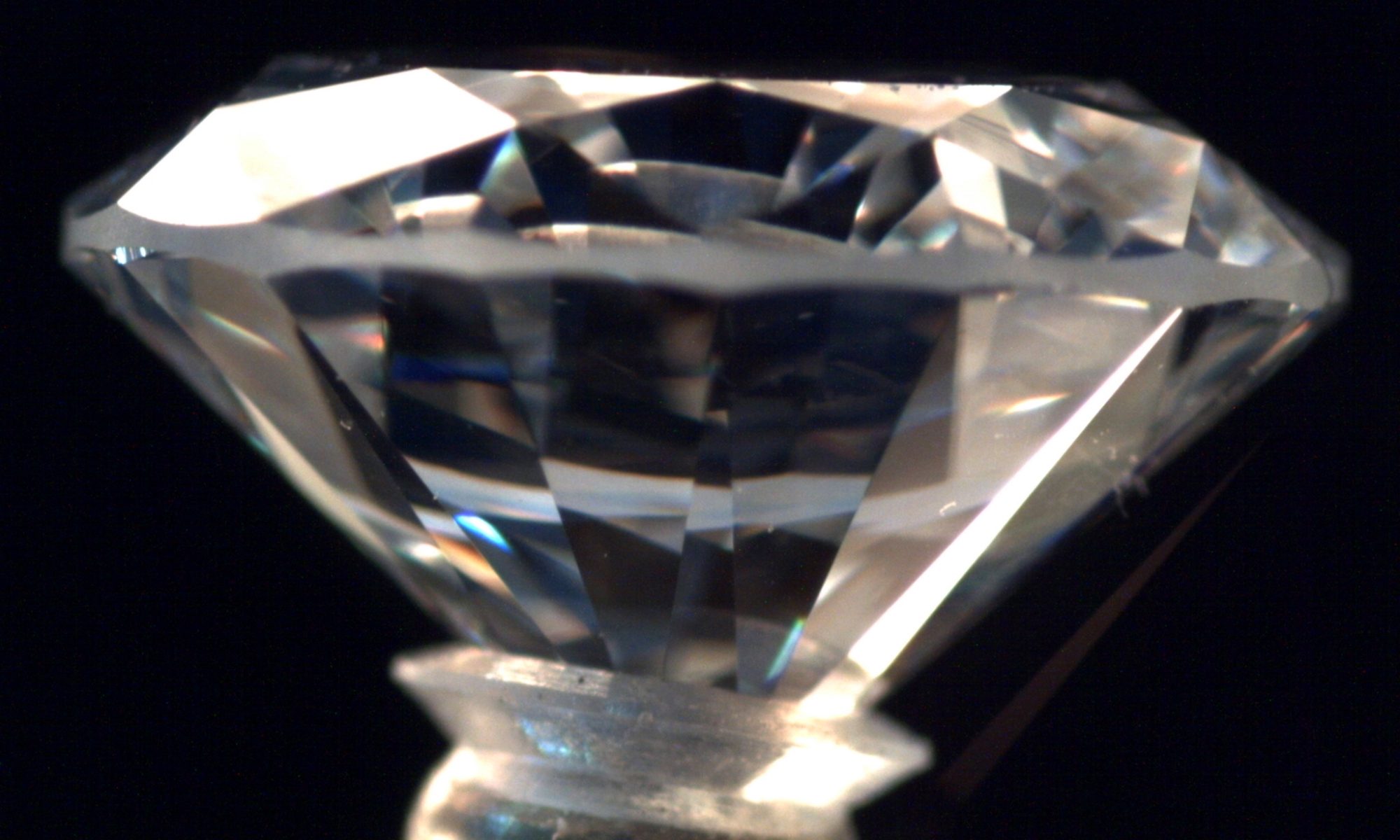
Girdle thickness refers to the width of the diamond’s girdle, which is the outer edge separating the crown (top) from the pavilion (bottom). It plays a crucial role in the diamond’s durability, setting security, and overall appearance.
A well-proportioned girdle ensures the diamond maintains structural integrity while maximising its face-up size and brilliance. If the girdle is too thin, it becomes prone to chipping, while an excessively thick girdle can add unnecessary carat weight without increasing the visual size.
How Girdle Thickness is Measured
Girdle thickness is usually assessed as a percentage of the average diameter of the diamond. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and other major gemological labs describe girdle thickness using standard terms, which range from extremely thin to extremely thick.
GIA Girdle Thickness Grading Scale
Girdle Thickness Description Impact on Durability & Appearance
Extremely Thin Very narrow and difficult to see. High risk of chipping, especially in prong settings.
Thin Slightly more visible but still delicate. Can be durable but may still chip with rough handling.
Medium Well-balanced thickness. Ideal for durability and brilliance.
Slightly Thick A little more pronounced but still proportionate. Generally safe and adds slight weight.
Thick Noticeably wider girdle. Adds weight without significant face-up size increase.
Very Thick A substantial edge, clearly visible. Makes the diamond appear smaller than its carat weight.
Extremely Thick Very broad, often visible from above. Adds excess carat weight with little aesthetic benefit.
How Girdle Thickness Affects a Diamond
1. Durability & Wear Resistance
Too Thin (Extremely Thin or Thin)
Prone to chipping or breaking, especially at points in fancy shapes (e.g., marquise, pear, princess cuts).
Less secure in settings that expose the girdle, such as prong settings.
Too Thick (Very Thick or Extremely Thick)
Reduces the likelihood of damage but adds extra weight to the diamond.
May require deeper prongs or bezel settings, limiting design options.
2. Diamond Size & Spread
A medium to slightly thick girdle allows a diamond to appear larger for its carat weight.
A thick to extremely thick girdle traps weight in the middle of the stone, making it look smaller than other diamonds of the same carat weight.
3. Light Performance & Brilliance
Ideal girdle thickness supports the proper reflection and refraction of light within the diamond.
Overly thick girdles can cause light leakage, reducing brilliance.
Uneven girdles (with varying thickness) can affect symmetry, leading to inconsistencies in sparkle.
Girdle Thickness in Different Diamond Shapes
Some diamond shapes naturally require thicker girdles for durability:
Diamond Shape Recommended Girdle Thickness Reason
Round Brilliant Thin to Slightly Thick Standard cut design maximises brilliance.
Princess Cut Medium to Slightly Thick Sharp corners need extra protection.
Marquise & Pear Slightly Thick to Thick Points are fragile and prone to chipping.
Oval & Cushion Thin to Medium Balanced proportions enhance sparkle.
Emerald & Asscher Medium to Thick Step cuts require sturdier girdles for protection.
Heart Shape Slightly Thick to Thick The cleft and point need reinforcement.
How to Choose the Best Girdle Thickness
Best for Durability: Medium to Slightly Thick (avoids chipping while maintaining beauty).
Best for Appearance & Spread: Thin to Medium (provides a larger face-up look).
Best for Value: Avoid extremely thick girdles that add unnecessary weight.
Always check a diamond’s girdle thickness in its grading report (e.g., GIA, DCLA) before purchasing.